
In 2025, manufacturers face mounting pressure to evolve. Traditional sales tactics can’t keep up with a world shaped by emerging manufacturing industry trends – including automation, AI, supply chain volatility, and rising customer expectations.
To stay competitive, companies must embed data-driven systems, embrace digital transformation, and build resilience into every layer of operations – from the factory floor to the customer experience.
6 Trends Reshaping Manufacturing in 2025
These six shifts are redefining how manufacturers operate, compete, and grow:
-
Automation is transforming production lines into data-driven ecosystems.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is powering predictive analytics, autonomous robotics, and smart decision-making across the supply chain.
-
Cybersecurity is becoming a core operational priority as digital exposure rises.
-
Supply Chain Resilience is shifting from a nice-to-have to a survival strategy.
-
Sustainability is moving from compliance to competitive differentiator.
-
Digital Transformation is changing how manufacturers connect with customers, design products, and deliver service.
Together, these trends are setting the foundation for smarter, leaner, and more future-ready manufacturing operations.
1. Automation: From Manual Fatigue to Scalable Smart Production
Manufacturers have long underutilized the operational data generated across their facilities. In 2025, the conversation has shifted from whether to automate to how intelligently you’re doing it.
AI-powered automation is enabling manufacturers to:
-
Predict and prevent machine failures
-
Reallocate labor from repetitive tasks to higher-value work
-
Optimize production schedules in real time
-
Reduce cycle times and operational bottlenecks
This isn’t hypothetical – real manufacturers are already seeing ROI.
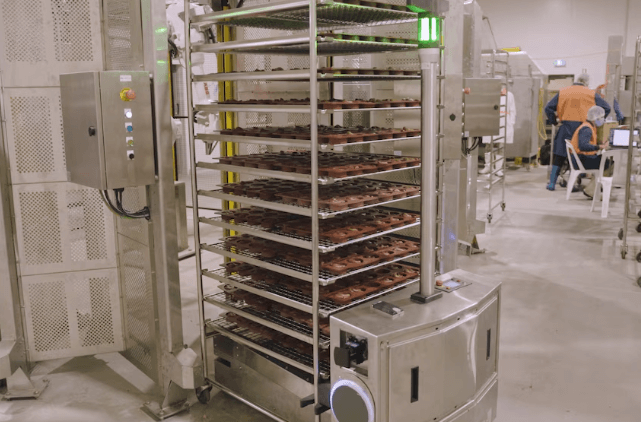

An autonomous mobile robot navigates the production floor at Priestley’s Gourmet Delights, optimizing internal logistics as part of their AI-driven manufacturing system.
In 2024, Priestley’s launched a $53 million AI-enabled smart factory in Queensland. The facility integrates autonomous intelligent vehicles and collaborative robots that transport products, stack baking trays, and optimize internal logistics. These AI systems also monitor equipment health to trigger predictive maintenance – reducing downtime and extending asset life.
As a result, the factory doubled production capacity, cut manual labor in half for repetitive tasks, and opened new skilled roles to manage and fine-tune the automated systems.
This is what smart manufacturing looks like: automation that scales without sacrificing agility.
2. AI: From Reactive Operations to Predictive Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept – it’s a competitive differentiator in today’s factories. In 2025, AI is being embedded across manufacturing operations to anticipate problems, accelerate production, and unlock new efficiencies that traditional systems can’t reach.
Manufacturers are using AI to:
-
Automate complex decision-making in real time
-
Detect and resolve quality issues before they escalate
-
Improve demand forecasting and inventory accuracy
-
Guide robots and machines with adaptive learning models
These capabilities are enabling faster response times, fewer errors, and higher margins.
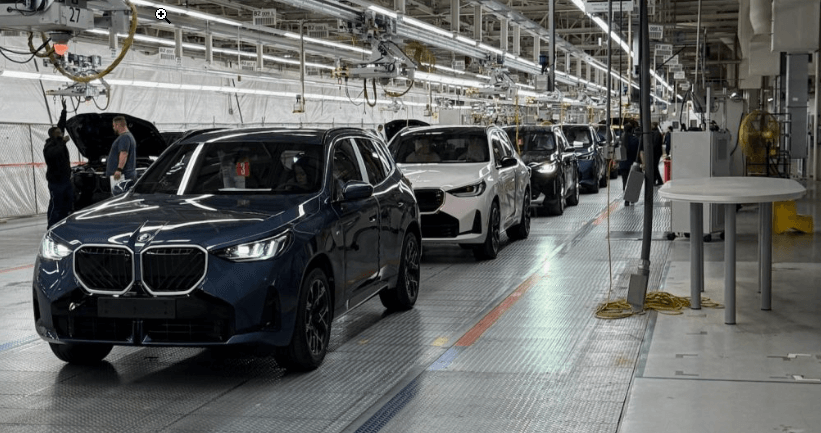

BMW’s Spartanburg plant integrates AI-managed robots to streamline production and cut costs by $1M annually.
At its Spartanburg facility in South Carolina – the largest BMW plant in the world – the automaker has integrated AI-managed robotics to optimize assembly line performance. These intelligent systems handle high-volume, repetitive tasks with precision, freeing up human workers for more complex, value-added responsibilities.
Since implementation, BMW has reported annual cost savings of approximately $1 million, along with significant improvements in production efficiency and error reduction. It’s a clear example of how AI isn’t just a tool – it’s an operational engine.
This is the next phase of manufacturing intelligence: AI that drives profitability through predictive precision.
3. Cybersecurity: Securing Smart Factories Against Expanding Threats
As manufacturers embrace automation, cloud platforms, and connected devices, they also expand their attack surface. In 2025, cybersecurity is no longer an IT problem – it’s a core operational risk.
Modern manufacturing environments are now hybrid systems combining legacy machinery with IoT sensors, AI algorithms, and remote monitoring. This convergence has created new vulnerabilities, especially in third-party vendor relationships and OT (operational technology) networks.
Key risks manufacturers face today:
-
Supply chain breaches introduced via vendors or contractors
-
Ransomware targeting industrial control systems (ICS)
-
Data leaks from cloud-based platforms used for collaboration
-
Internal sabotage or misconfigured access controls in smart factories
Studies suggest that 98% of organizations now work with at least one third-party vendor that has experienced a data breach.
While not recent, the 2019 ransomware attack on aluminum giant Norsk Hydro remains a critical reference point. A LockerGoga infection forced Hydro to shut down multiple plants across Europe and switch to manual operations. The incident cost over $70 million in damages – but Hydro’s transparent response and investment in cybersecurity rebuilding have since made them a benchmark in industrial cyber resilience.
The takeaway for 2025? If your factory is getting smarter, your security posture has to scale with it. Manufacturers must invest in layered defenses, segment OT from IT networks, and vet all third-party integrations with the same scrutiny as internal systems.
4. Supply Chain Resilience: From Efficiency to Survival Strategy
The supply chain disruptions of the past five years—pandemic shutdowns, geopolitical shocks, raw material shortages, and shipping gridlock—have made one thing clear: efficiency alone is not enough.
In 2025, manufacturers are rethinking how they source, store, and distribute. Resilience has become a core competitive strategy, not a contingency plan.
Key resilience strategies include:
-
Diversifying suppliers across regions to reduce geopolitical dependency
-
Onshoring or nearshoring critical manufacturing to stabilize fulfillment
-
Investing in supply chain visibility through IoT, ERP integrations, and real-time analytics
-
Building inventory buffers for high-risk components or markets
-
Scenario planning to model and prepare for multi-point disruptions
According to McKinsey, supply chain disruptions lasting a month or longer now occur every 3.7 years on average – costing manufacturers millions per event.
Cisco has long embraced a multi-tiered supply chain model, but in response to increasing volatility, it’s doubled down on digital transparency. By investing in predictive analytics and building visibility deep into its second- and third-tier suppliers, Cisco can now identify at-risk nodes before they become bottlenecks. This foresight allows them to reroute logistics or shift procurement in real time – minimizing disruption without overstocking.
For manufacturers in 2025, supply chain resilience isn’t about being reactive – it’s about being structurally adaptable in a world where instability is the norm.
5. Sustainability: From Compliance to Competitive Advantage
Environmental performance has evolved from a regulatory checkbox to a strategic imperative. In 2025, manufacturers are not only meeting sustainability standards but leveraging them as a competitive edge.
Key sustainability strategies include:
-
Electrifying operations and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
-
Implementing closed-loop production systems to minimize waste.
-
Redesigning packaging to comply with stricter material regulations.
-
Tracking emissions across Scope 1, 2, and 3 footprints.
-
Publishing sustainability metrics in supplier scorecards and ESG reports.
 In many sectors, sustainability is now a prerequisite to even being considered for supplier contracts – especially in automotive, consumer electronics, and energy.
In many sectors, sustainability is now a prerequisite to even being considered for supplier contracts – especially in automotive, consumer electronics, and energy.
Unilever has committed to reducing its use of virgin plastic by 50% by 2025 and aims to use at least 25% recycled plastic in its packaging. By the end of 2023, the company had reduced its use of virgin plastic by 18% compared to its 2019 baseline, and 22% of its global product portfolio used recycled plastic.
Additionally, Unilever is investing in renewable energy and water conservation efforts across its manufacturing sites, aiming to reduce water use in manufacturing by 50% per ton of production by 2025.
For manufacturers in 2025, sustainability isn’t just about compliance – it’s about building a resilient and forward-thinking business model that aligns with global environmental goals.
6. Digital Transformation: Empowering the Self-Service Buyer
In 2025, digital transformation is about more than upgrading legacy systems – it’s about rethinking how manufacturers interact with customers across channels. The modern buyer expects instant access to product information, intuitive navigation, and the ability to self-educate without talking to sales.
Leading manufacturers are using digital tools to:
-
Streamline product discovery across SKUs and variants
-
Enable real-time updates without reprinting
-
Reduce reliance on PDF downloads or physical brochures
-
Embed catalogs directly into websites or email campaigns
Interactive digital catalogs help manufacturers cut printing costs and improve buyer engagement.
DCatalog helps manufacturers transform traditional product sheets into dynamic, branded digital catalogs. These assets can be embedded into websites, shared via link, and updated in real-time – no coding required. The result is a better buyer experience, faster quoting cycles, and increased visibility into product engagement.
In a landscape where 82%+ of B2B buyers ordering or paying through digital commerce (source: Gartner), tools like DCatalog enable manufacturers to meet expectations without scaling sales headcount.
This is what modern go-to-market enablement looks like: digitized content that converts interest into action.
Turning Trends Into Strategy: What Manufacturers Should Do Now
Recognizing the top manufacturing industry trends is only the first step – acting on them is where competitive advantage is built.
Manufacturers that succeed in 2025 will translate trend awareness into operational execution by:
-
Implementing a data strategy that supports predictive decision-making
-
Adopting AI tools to automate quality control and optimize production in real time
-
Digitizing product catalogs to meet customer expectations for self-service and seamless access
-
Upskilling teams to thrive in a data-driven, fast-adapting environment
-
Investing in sustainability not just for compliance, but as a lever for cost reduction and brand differentiation
Each of these trends isn’t a siloed initiative – they reinforce one another. AI makes automation smarter. Data strategy makes digital transformation measurable. Sustainability drives innovation, not just reporting. The manufacturers that integrate these efforts holistically will lead the next chapter of industry growth.
Final Thought: Adapt Faster. Engage Smarter.
In a manufacturing landscape where speed, intelligence, and customer alignment define success, it’s no longer enough to optimize what already exists – you have to rethink how value is created and delivered.
DCatalog helps manufacturers do exactly that.
By transforming static product sheets into interactive, digital-first catalogs, DCatalog enables faster sales cycles, stronger buyer engagement, and real-time product updates – all without adding complexity to your tech stack.
- Create branded, searchable catalogs
- Embed them directly into your site or email campaigns
- Reduce manual errors and eliminate outdated PDFs
See it in action – Reach out to one of our Publishing Executives today, or sign up for a free trial to experience our platform for yourself.

